Eczema on Black Skin: How to Identify & Treat Different Types
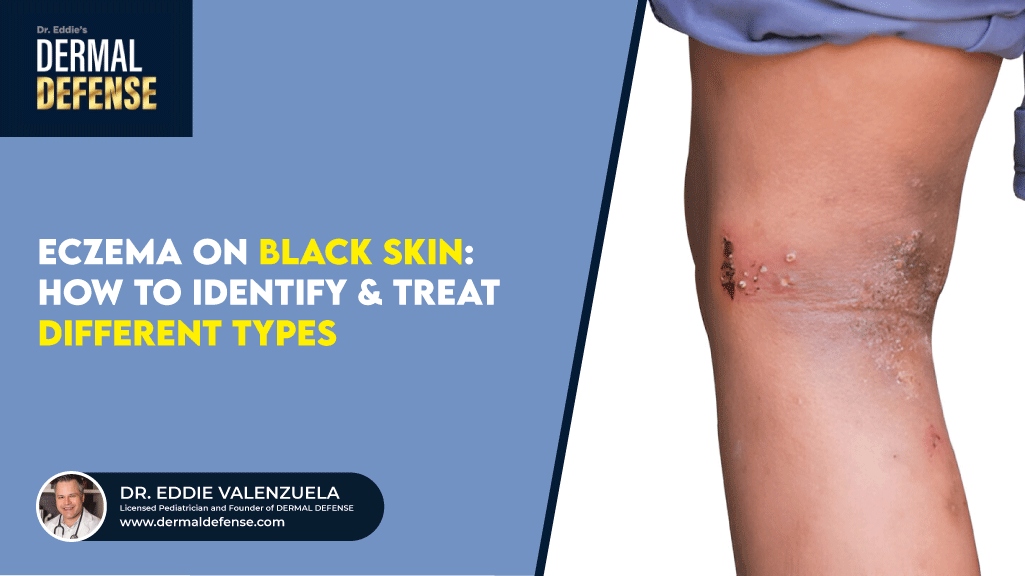
Eczema is a chronic and potentially severe skin condition characterized by rash-like symptoms. Its symptoms and causes vary. Varies with age, intensity, and even ethnicities. This is why some people ask if eczema on black skin is different from eczema on white skin.
We created this guide to inform you of this skin condition, its causes and symptoms, types, effects on black skin, management, and preventive measures.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema is a group of chronic skin conditions that cause inflammation, itching, and irritation. It is sometimes referred to as dermatitis, with atopic dermatitis being the most common form. While eczema is not contagious, it can be long-lasting and tends to flare up periodically.
The condition causes red, dry, and itchy patches that can appear anywhere on the body, most often on the face, scalp, hands, legs, skin folds, and behind the knees. In more severe cases, the skin may crack, ooze, or become thickened over time.
Eczema can affect people of any age or gender, but it is most common in children under the age of five. Some children may outgrow it, while others continue to experience symptoms into adulthood.
There are several different types of eczema, each with its own triggers and patterns, but all share one thing in common: they require consistent care and management to keep the skin barrier healthy and prevent flare-ups.
What Does Eczema Look Like on Black Skin?
Eczema can look different on darker skin tones compared to lighter ones, which sometimes makes it harder to recognize or diagnose early. Instead of appearing red or pink, eczema patches on Black or brown skin may look purple, gray, dark brown, or ashen.
While inflammation is still present, it may be less visibly red, and areas of dryness or thickened skin can appear darker than the surrounding skin. In some cases, after inflammation heals, it can leave behind areas of lighter or darker pigmentation, a condition called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
Because these color changes can mask early signs of eczema, diagnosis and treatment are sometimes delayed, which may lead to more severe flare-ups. This is one reason why people of color may experience more intense symptoms or longer-lasting discoloration even after the eczema clears.
Early identification and proper care, using fragrance-free, gentle cleansers and rich moisturizers, are essential for managing eczema effectively on all skin tones.
How to Identify Eczema on Balck Skin?
Recognizing eczema on Black or brown skin can be more challenging because inflammation doesn’t always appear red as it does on lighter skin tones. However, by understanding how eczema looks and feels on darker complexions, it becomes easier to identify and treat it early.
Common Signs and Symptoms
While symptoms vary from person to person, eczema on Black skin often includes:
- Inflammation or swelling of the affected areas
- Color changes (may appear purple, dark brown, gray, or ashen instead of red)
- Itching, which can range from mild to intense
- Dryness and flaking
- Rash or rough, scaly patches
- Oozing or crusting in severe flare-ups
- Cracked or thickened skin with chronic irritation
Because mild cases may be less visibly red, eczema on darker skin is sometimes underdiagnosed. If you suspect eczema, it’s best to see a dermatologist experienced with skin of color for proper evaluation and treatment.
Differences in Color and Pigmentation Changes
Eczema can cause discoloration or uneven skin tone as it heals. On darker skin, inflammation may leave purple, gray, or brown patches, while healing areas can appear lighter or darker than the surrounding skin (a condition known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation).
These color changes are temporary but may take weeks to months to fade. Avoid scratching or using harsh products, which can worsen pigment changes.
Itching, Dryness, and Thickening
Eczema-prone skin is extremely dry, which can make it look dull or ashy. Repeated scratching can lead to skin thickening (lichenification) and even small cracks that sometimes bleed. Itching can be intense enough to disturb sleep or daily comfort.
To manage these symptoms, focus on gentle daily cleansing and deep hydration using fragrance-free, eczema-safe products to restore moisture and calm irritation.
What causes eczema on black skin?

There is no single cause of eczema. It’s a complex condition influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that affect the skin’s protective barrier and immune response. Understanding these triggers can help prevent flare-ups and manage symptoms more effectively, especially for people with darker skin tones, where early signs may be harder to spot.
1. Genetic Factors
Eczema often runs in families. People with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma have a higher risk of developing the condition. This is because they may inherit a weakened skin barrier, making their skin more sensitive to irritants and allergens.
While genetics cannot be changed, consistent skincare and trigger management can significantly reduce flare-ups and help maintain healthier skin over time.
2. Environmental Factors
The environment plays a major role in eczema flare-ups. Cold, dry weather can deplete the skin’s natural moisture, leading to cracking and irritation. Meanwhile, hot and humid conditions can trap sweat and encourage bacterial or yeast overgrowth.
Other common environmental triggers include:
- Sudden temperature or humidity changes
- Air pollutants and smoke exposure
- Harsh soaps, detergents, or fragrances
- Seasonal allergens like pollen or mold
People with darker skin tones may also experience more persistent discoloration after inflammation, so minimizing environmental triggers helps reduce both irritation and pigment changes.
3. Lifestyle and Skincare Habits
Everyday habits can also influence how eczema behaves. Tight clothing, heavy sweating, or excessive friction can irritate the skin and worsen symptoms. Additionally, using harsh or fragranced skincare products can trigger allergic or inflammatory responses.
To reduce the risk of flare-ups:
- Wear loose, breathable fabrics like cotton.
- Avoid overheating and prolonged sweating.
- Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers designed for sensitive skin.
- Maintain a balanced diet and manage stress, both of which support skin and immune health.
Eczema affects all skin tones, but its appearance and the consequences of its appearance, like post-inflammatory discoloration, can differ on darker skin. By understanding and managing your unique triggers, you can minimize flare-ups and keep the skin barrier strong and hydrated.
Managing Eczema on Black Skin
Eczema can lead to dryness, irritation, and uneven tone on darker skin, but with the right skincare routine, these concerns can be managed and comfort restored. The goal is to support the skin barrier, maintain hydration, and keep skin looking and feeling healthy.
Over-the-Counter Creams and Ointments
A dermatologist-recommended or eczema-friendly moisturizer can help replenish hydration and protect sensitive skin. One example is the Dermal Defense Eczema Moisturizing Cream, created by Dr. Eddie, a board-certified pediatrician dedicated to developing gentle, effective skincare for sensitive and eczema-prone skin.
This fragrance-free cream is formulated to nourish dry skin, restore softness, and help strengthen the skin’s natural barrier—making it suitable for daily use on all skin tones. With regular use, skin can feel more comfortable, smoother, and visibly healthier.
For best results, apply after cleansing to help seal in moisture and support long-lasting hydration.
Skincare Tips for Managing Eczema on Black Skin

Caring for eczema-prone skin, especially on darker skin tone, requires a routine that focuses on gentle cleansing, deep hydration, and avoiding triggers. Because eczema can cause dryness, irritation, and discoloration, consistency in daily care is key to maintaining comfort and healthy-looking skin.
1. Cleansing the Skin
Clean skin is the foundation of good eczema care. Even when receiving treatment, it’s important to remove impurities, sweat, and bacteria that can aggravate the condition.
Choose a soap-free, fragrance-free body wash designed for sensitive skin—one that cleanses without stripping natural oils. Look for products that contain moisturizing and soothing ingredients, so cleansing supports the skin barrier instead of drying it out.
A gentle, dermatologist-developed formula such as the Dermal Defense Sensitive Skin Body Wash can be used daily to cleanse and hydrate at the same time.
2. Choosing the Right Moisturizer
Cleansing alone isn’t enough. Eczema-prone skin needs moisture to stay comfortable. After washing, apply an eczema-friendly moisturizer such as the Dermal Defense Eczema Moisturizing Cream.
Use it twice daily, especially after bathing, to help lock in moisture and support the skin’s natural barrier. The combination of a gentle body wash and daily moisturizer helps the skin stay soft, supple, and balanced.
3. Avoiding Harsh Chemicals and Fragrances
Many soaps, detergents, and skincare products contain fragrances, dyes, or alcohols that can irritate eczema-prone skin. Fragrance-free, hypoallergenic formulations are best.
When in doubt, check the label and avoid unnecessary additives. Using products designed for sensitive skin, like those in the Dermal Defense eczema care line, helps minimize irritation and maintain a healthy appearance.
4. Clothing and Fabric Considerations
What you wear can directly affect your skin. Tight, synthetic fabrics trap heat and sweat, which can lead to irritation. Choose light, breathable fabrics that allow air circulation and reduce friction.
Dermatologists often recommend natural or ultra-soft materials such as:
- Cotton
- Bamboo
- Modal
- Silk
- Lyocell (TENCEL)
5. Preventing Eczema Flare-Ups
To keep eczema symptoms under control and reduce the chance of flare-ups, follow these practical tips:
- Avoid excessive heat and humidity.
- Skip long, hot showers. Use cool or lukewarm water instead.
- Keep baths short and gentle.
- Wear breathable, lightweight clothing.
- Stay hydrated and drink plenty of water.
- Moisturize multiple times daily, especially after bathing.
- Reduce stress levels through rest, exercise, or mindfulness.
- Avoid fragranced or harsh beauty products.
6. When to See a Doctor
If your symptoms persist or worsen, seek professional guidance. You should consult a dermatologist if:
- Eczema is spreading or getting worse,
- Over-the-counter products are not helping,
- You notice oozing, pus, or signs of infection, or
- Flare-ups are interfering with sleep or daily activities.
Conclusion
Eczema affects all skin tones, but on Black or brown skin, inflammation and redness can be harder to see, leading to delayed diagnosis and more noticeable discoloration after healing. Recognizing the signs early and maintaining a consistent skincare routine, centered on gentle cleansing and daily moisturization, can help you keep your skin comfortable and balanced.
While eczema cannot be permanently cured, the right products and habits can make a visible difference in the look, feel, and resilience of your skin.
Dermal Defense Eczema Care Routine
Consistency is the key to keeping eczema-prone skin healthy and comfortable. For best results, follow this simple two-step dermatologist-inspired routine designed for sensitive skin:
Step 1: Cleanse Gently
Start with the Sensitive Skin Body Wash.
Formulated without soap, fragrance, or harsh surfactants, this gentle cleanser removes impurities while helping skin feel soft and hydrated after every wash.
Step 2: Moisturize Deeply
After cleansing, apply the Eczema Moisturizing Cream.
This dermatologist-developed cream helps replenish moisture and support the skin’s natural barrier, leaving it smoother and more comfortable throughout the day.
Both products are created by Dermal Defense, a brand committed to gentle, science-backed skincare solutions for sensitive and eczema-prone skin.
FAQs About Eczema on Black Skin
Can eczema go away on its own?
Eczema is a chronic condition that requires ongoing care. Without treatment, symptoms can worsen or recur more frequently.
Is eczema permanent?
No. With proper skincare and medical guidance, flare-ups can be managed, and the skin can return to a healthy state.
Is eczema more common in Black communities?
Eczema occurs across all skin tones, but research suggests that severity may be higher in Black children due to delayed diagnosis and differences in how inflammation appears on darker skin.
Does eczema cause permanent dark spots on Black skin?
Not usually. Discoloration from eczema, known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, is temporary, though it can take time to fade. Avoid scratching to reduce the risk of pigment changes.
How much does diet affect eczema?
Diet alone doesn’t cause eczema, but certain foods (like eggs, peanuts, soy, fish, or citrus) can trigger flare-ups in sensitive individuals. Track reactions and discuss with your dermatologist before eliminating foods.
Can stress worsen eczema?
Yes. Stress can disrupt the skin’s barrier and immune response, making eczema flare-ups more likely. Managing stress through sleep, exercise, or mindfulness can help maintain healthy skin.
- Eczema and Mental Health: How It Affects Anxiety & Depression - January 29, 2026
- Eczema and Genetics: Is It Hereditary? - January 29, 2026
- Is Eczema Contagious? Debunking Myths - January 27, 2026
